Department of Bariatric And Diabetes Surgery
Obesity is a serious medical condition that can cause dangerous health problems, such as high blood pressure, Type 2 Diabetes, severe arthritis, life-threatening sleep apnea, and heart and lung disease.
Weight-loss surgery can change your life.
For many patients struggling with obesity, the usual diet-and-exercise prescription just doesn’t work. If you feel this frustration, you’ve come to the right place “BIMS BARIATRICS AND METABOLIC SURGERY CENTR” WE PROVIDE A to Z solution for your Obesity and Diabetes….
At OUR CENTRE, our program is focused on addressing obesity with modern scientific treatment strategies, research, and education. The comprehensive program includes:
- Clinical Pathway and Evaluation of Patient.

- Psychological evaluation
- Nutrition and dietary counseling for life
- Exercise & Fitness
- Weight loss surgery seminars
- Medical weight loss program.
- Patient support groups
- A lifetime of support to help you on your path to a new lifestyle

We support you all the way.
Our skilled and caring Bariatric Surgery team supports you before your surgery – and long after. For months, even years after your surgery, we offer you encouragement and personalized success strategies for reaching and maintaining your weight-loss goal.
I am ready for the Bariatric -weight-loss surgical option, What next?
Our Expert Team Will Support You Every Step of the Way
The BIMS Bariatric & Diabetes Surgery Program is composed of a multidisciplinary team of Bariatric specialists who provide personalized treatment, committing to years of follow-up care and supporting your effort to maintain a healthy weight, while meeting your nutritional needs.
The process you will follow involves several phases:
You will meet with the surgeon to evaluate whether surgery is right for you. The surgeon will provide information about the procedure and answer any questions you may have.
Our team of specialists, including a nutritionist, radiologist, pulmonologist, cardiologist, and psychiatrist, will perform comprehensive medical exams and evaluations. You will also be asked to attend intensive education and support group programs to learn what to expect during and after surgery.
Board-certified skilled surgeons trained in advanced laparoscopic surgery and bariatric care will work closely with anesthesiologists and highly trained operating room staff who are familiar with the special needs of bariatric patients.
Nurses trained in post-bariatric surgical care will work to prevent and manage possible complications. The surgeon, bariatric nurses, and nutritionist will follow you carefully throughout recovery.
you must commit to making profound lifestyle changes. To help meet this challenge successfully and safely, you will be closely monitored for nutritional deficiencies and will receive free counseling to help you manage post-operative dietary requirements. You will continue to attend our free support group meetings.
Who could be a candidate for bariatric surgery?
- Patients considering surgery should have already tried to lose weight by other methods. Surgery is not the first choice for weight management. When other methods are not successful and obesity is a threat to health, it is time to learn about surgical options.
- Motivation to change habits and a commitment to lifelong diet modifications and exercise are necessary when undergoing bariatric surgery. Surgery is only one tool. Success depends on following diet and exercise recommendations after surgery.
- Patients with a BMI of 35 to 40 (32.5 – 37.5 for Asia-Pacific countries) are considered for surgery when they also have an obesity-related illness like diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea.
- Patients with a BMI over 40 (>37.5 for Asia-Pacific countries) are eligible for surgery based on weight alone.
Who should not have surgery?
- People who cannot adhere to the necessary pre-and postoperative dietary changes should not have bariatric surgery.
- People with a substance abuse problem will not be considered for this operation.
- People with an eating or psychiatric disorder that is untreated or unresolved are not surgical candidates. If these conditions are resolved or well-controlled, and clearance is received from a psychologist, surgery can be considered.
- Women planning a pregnancy in the near future should not undergo surgery.
- Patients with health conditions making them medically high-risk should avoid surgery.
How Does Weight loss surgery work?
The principle of this weight loss surgery is to confine the intake of food and drink and to limit the absorption of the food in the intestine. This reduction of nutrients and calorie absorption enables the patient to lose weight. In this modern medical era, some teens and adults are potential patients for minimally invasive laparoscopic bariatric surgery. This is more advantageous than the other types of weight loss surgery options.
Laparoscopic Bariatric surgery (weight-loss surgery) includes a variety of procedures performed on people who are obese. This weight-loss operation proceeds by reducing the size of the stomach with an implanted medical device (gastric banding) or through the removal of a portion of the stomach (sleeve gastrectomy) or by resecting and re-routing the small intestines to a small stomach pouch (gastric bypass surgery).
Operations for obesity
Bariatric surgical procedures cause weight loss by restricting the amount of food the stomach can hold, causing malabsorption of nutrients, or by a combination of both gastric restriction and malabsorption. Bariatric procedures also often cause hormonal changes. Most weight-loss surgeries today are performed using minimally invasive techniques (laparoscopic surgery).
The most common bariatric surgery procedures are gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric band, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Each surgery has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The main surgical techniques are;
Combination of metabolic and restrictive
- Combination of metabolic and restrictive
- Mini Gastric Bypass(MGB)
- Sleeve gastrectomy with Proximal Jejunal Bypass (LSG+PJB)
Restrictive only
- Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG)
- Gastric Band Plication (LAGBP)
Metabolic Surgery:
Particularly for the obesity with Type 2 DM
- Loop Duodeno-jejunal bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy(LDJB-SG)
Lap Adjustable Gastric Band plication [LAGBP]:
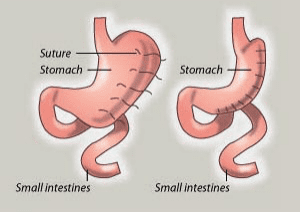
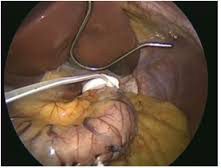
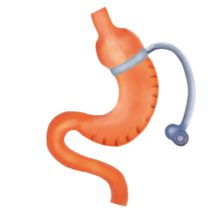
This is the newest Restrictive type of weight loss procedure. Mostly suitable for patients with BMI 35-50. This is invented by Dr. C.K.Huang from Taiwan. Unlike gastric bypass surgery, gastric sleeve Plication surgery does not require the resection of a portion of the stomach. Instead, it preserves the healthy tissue and its functionality by suturing/plicating the stomach in folds rather than removing a portion of it. With this procedure, the stomach is dissected on one side, which allows the surgeon to access both the front and back surfaces of the stomach. One side of the stomach is folded and fastened in two different layers. The folds narrow and reduce the available volume of the stomach, limiting how much the patient can eat at one time.
The major change to your anatomy is that the stomach lining is folded in upon itself. After the Plication of the stomach, there is the placement of Adjustable silicon Gastric Band around the upper part of the stomach by par Placida technique. this band will help to check the overeating by the patient by acting as an adjustable band to sound the stomach entry. This will help to induce fast weight loss and also reduces the chances of weight regain issue of only gastric plication and only gastric banding alone. The intestines are not manipulated at all, which allows for complete absorption of calories, nutrients, vitamins, and minerals.
Advantages
- There is no removal or cut of stomach tissue
- The procedure is completely reversible and revisable
- No malabsorption/ dumping syndrome.
- Less risk of Protein/ vitamin deficiencies.
- The risk of short time complications is lower
- The procedure doesn’t require staples, meaning there is no possibility for leaking, bleeding, or rejection of a foreign object at the closure site.
- Less expensive.
Disadvantages:
- Recovery time might be longer than the gastric sleeve
- The success rate is lower than the gastric sleeve and bypass procedures
- The hormone of hunger “Ghrelin” is not removed with the surgery
- Band adjustment requires frequent follow-up.
- The band is acts as the foreign body so some time chances of rejection and infection.
Sleeve Gastrectomy
The Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy – often called the sleeve – is performed by removing approximately 75-80% of the stomach. The remaining stomach is a tubular pouch that resembles a banana.
The Procedure
This procedure works by several mechanisms. First, the new stomach pouch holds a considerably smaller volume than the normal stomach and helps to significantly reduce the amount of food (and thus calories) that can be consumed. The greater impact, however, seems to be the effect the surgery has on gut hormones that impact a number of factors including hunger, satiety, and blood sugar control.
Short term studies show that the sleeve is as effective as the roux-en-Y gastric bypass in terms of weight loss and improvement or remission of diabetes. There is also evidence that suggests the sleeve, similar to the gastric bypass, is effective in improving type 2 diabetes independent of weight loss. The complication rates of the sleeve fall between those of the adjustable gastric band and the roux-en-y gastric bypass.
Advantages
- Restricts the amount of food the stomach can hold
- Induces rapid and significant weight loss that comparative studies find similar to that of the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Weight loss of >50% for 3-5+ year data, and weight loss comparable to that of the bypass with the maintenance of >50%
- Requires no foreign objects (AGB), and no bypass or re-routing of the food stream (RYGB)
- Involves a relatively short hospital stay of approximately 2 days
- Causes favorable changes in gut hormones that suppress hunger, reduce appetite, and improve satiety
Disadvantages
- Is a non-reversible procedure
- Has the potential for long-term vitamin deficiencies
- Has a higher early complication rate than the AGB
- Weights regain issue.
The Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass – often called gastric bypass – is considered the ‘gold standard’ of weight loss surgery.
The Procedure
There are two components to the procedure. First, a small stomach pouch, approximately one ounce or 30 ml in volume, is created by dividing the top of the stomach from the rest of the stomach. Next, the first portion of the small intestine is divided, and the bottom end of the divided small intestine is brought up and connected to the newly created small stomach pouch. The procedure is completed by connecting the top portion of the divided small intestine to the small intestine further down so that the stomach acids and digestive enzymes from the bypassed stomach and first portion of the small intestine will eventually mix with the food.
The gastric bypass works by several mechanisms.
First, similar to most bariatric procedures, the newly created stomach pouch is considerably smaller and facilitates significantly smaller meals, which translates into fewer calories consumed. Additionally, because there is less digestion of food by the smaller stomach pouch, and there is a segment of the small intestine that would normally absorb calories as well as nutrients that no longer has food going through it, there is probably to some degree less absorption of calories and nutrients.
Most importantly, the rerouting of the food stream produces changes in gut hormones that promote satiety, suppress hunger, and reverse one of the primary mechanisms by which obesity induces type 2 diabetes.
Advantages
- Produces significant long-term weight loss (60 to 80 percent excess weight loss)
- Restricts the amount of food that can be consumed
- May lead to conditions that increase energy expenditure
- Produces favorable changes in gut hormones that reduce appetite and enhance satiety
- Typical maintenance of >50% excess weight loss
Disadvantages
- Is technically a more complex operation than the AGB or LSG and potentially could result in greater complication rates
- Can lead to long-term vitamin/mineral deficiencies particularly deficits in vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and folate
- Generally has a longer hospital stay than the AGB
- Requires adherence to dietary recommendations, life-long vitamin/mineral supplementation, and follow-up compliance
Mini-gastric bypass
Mini”- gastric bypass is a newer operation that is also called by various other names such as “loop gastric bypass”, “omega-loop gastric bypass” or “single anastomosis gastric bypass”. It is a simplified version of the gastric bypass that has recently started to be performed in many countries around the world. Because of its more recent introduction, our understanding and confidence in its longer-term results are still developing.
It differs from a standard gastric bypass in that it involves the surgeon making a long sleeve a pouch of the stomach and only one joins between along stomach pouch and the small intestine. here small intestine is bypassed around 200-300cm according to the patient morbid obesity and metabolic syndrome. It functions in almost an identical way to the standard gastric bypass. Because of the absence of a second join, there is a slightly higher risk that some patients will experience troublesome reflux after this surgery. But also, because this second join is not present, it reduces the risk of longer-term complications such as intestinal obstruction. It is also quicker and easier to perform than standard gastric bypass. Many weight loss surgeons around the world are now starting to report their experience with the mini-gastric bypass and the results are very similar to standard gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. We expect that this type of surgery will become more widely used over the next few years.
Lap Sleeve Gastrectomy with Proximal Jejunal bypass: [LSG+PJB]
It is a novel technique of restrictive+malabsorptive procedure, a simpler and effective alternative to RYGB, with comparable short-term results. The procedure involves performing a regular sleeve gastrectomy with the addition of proximal jejunal bypass of 250-300 cm from the angle of Treitz and making anastomosis of jejunoileal anastomosis. The procedure is very safe and effective as a revision bariatric procedure for a failed sleeve gastrectomy or as a primary procedure in a patient with a BMI>45 in place of LSG.
Loop Duedono-Jejunal bypass with Sleeve gastrectomy [LDJB-SG]:
Sleeve gastrectomy with Loop Duodenal-Jejunal bypass– abbreviated as LDJB-SG is a procedure with two components. First, a smaller, tubular stomach pouch is created by removing a portion of the stomach, very similar to the sleeve gastrectomy. Next, a large portion of the small intestine is bypassed.
The Procedure
First, the conventional sleeve gastrectomy was done. after that, the duodenum (the first portion of the small intestine) is divided just past the outlet of the stomach. A segment of the distal small intestine- distal jejunum (200-300 cm ) is then brought up and connected as omega loop fashioned to the outlet of newly created cut part of proximal duodenum so that when the patient eats, the food goes through a newly created tubular stomach pouch and duodenum, then empties directly into the last segment of the small intestine. Roughly 200-300cm of the small intestine is bypassed by the food stream.
Similar to the other surgeries described above, the LDJB-SG initially helps to reduce the amount of food that is consumed; however, over time this effect lessens and patients are able to eventually consume near “normal” amounts of food. Unlike the other procedures, there is a significant amount of small bowel that is bypassed by the food stream.
This results in a significant decrease in the absorption of calories and nutrients (particularly protein and fat) as well as nutrients and vitamins dependent on fat for absorption (fat-soluble vitamins and nutrients).
Lastly, the LDJB-SG, similar to the gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy, affects guts hormones in a manner that impacts hunger and satiety as well as blood sugar control. The LDJB-SG is considered to be the most effective surgery for the treatment of diabetes among those that are described here.
Advantages
- Results in greater weight loss than RYGB, LSG, or AGB, i.e. 60 – 70% percent excess weight loss or greater, at 5 years follow up
- Allows patients to eventually eat near “normal” meals
- Reduces the absorption of fat by 70 percent or more
- Causes favorable changes in gut hormones to reduce appetite and improve satiety
- Is the most effective against diabetes remission and control compared to RYGB, LSG, and AGB
- No dumping syndrome and reflux issue.
Disadvantages
- Requires a longer hospital stay than the AGB or LSG.
- Long-term deficiencies of vitamins and minerals, i.e. iron, calcium, zinc, fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin D.
- Compliance with follow-up visits and care and strict adherence to dietary and vitamin supplementation guidelines are critical to avoiding serious complications from protein and certain vitamin deficiencies.
Medical Weight-Loss Management
For patients who choose not to undergo surgery and for those who are ineligible for surgery, the BIMS BARIATRICS AND DIABETES SURGERY CENTRE offers medical management for weight loss.
Candidates for medical weight-loss management include:
- Patients who decide bariatric surgery is not for them
- Patients with a BMI not high enough to be eligible for surgery
- Patients with a medical condition that prohibits surgery
- Patients whose insurance companies require their enrolment in a medical-management program prior to receiving bariatric surgery
- Surgical patients in other departments (such as for organ transplantation or orthopedic surgery) who need to lose weight prior to their operation
- Patients whose insurance companies don’t cover bariatric surgery
Medical weight-loss management at “BIMS” includes a team of specialists knowledgeable on all facets of weight loss and centers around five mainstays: TREATMENTS ARE TAILORED TO MEET THE NEEDS OF EACH INDIVIDUAL CASE
Diet:
Your physician and dietician will work together to develop a personalized eating plan that meets your nutritional and weight-loss needs and fits your lifestyle. All plans encourage healthy eating habits that you can maintain for life.
Exercise:
Each patient will receive a physician-designed exercise program that is customized to your needs and current fitness level. From pedometer-based programs to seated exercises, these plans will encourage you to get motivated and active. Consultations will include exercise demonstrations when needed and physical therapy sessions when necessary.
Behavior Modification:
A healthy lifestyle promotes healthy behaviors. If you suffer from depression or have an eating disorder, are a smoker, or have another addiction, psychologists are available to help you with important lifestyle changes that will improve your overall health and promote weight loss.
Lab and Diagnostic Evaluations:
You will receive an evaluation for all obesity-related diseases and your treatment will include continual monitoring of relevant data, including liver, kidney, and thyroid function; cholesterol; blood pressure; and metabolic syndrome.
Medications:
A physician will review any medications you are currently taking to ensure none has any side effects that are counterproductive to your weight-loss goals. When appropriate, medications taken for other conditions will be switched to alternatives that are more conducive to weight loss.
Medications such as appetite suppressants also may be prescribed, when appropriate, to patients meeting organ-health and lifestyle requirements. All weight-loss medications are prescribed according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) guidelines.
BIMS BARIATRICS Comprehensive Program Offers:
BIMS Bariatric Surgery Program provides full support for patients before, during, and after weight loss surgery. A registered dietitian and Nutritionist, who specializes in bariatric nutrition, works one-on-one with weight loss surgery patients during this time.
Because weight loss surgery changes the digestive process, nutritional counseling is essential to learning new techniques for eating. For patients who undergo gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y), the dietitian provides education and tools about food intolerances and avoiding nutritional deficiencies.
Upon approval for the surgery, you will attend a nutrition class that focuses on post- surgery nutritional guidelines. Additional classes are available at six weeks, six months, and one year after surgery. You may attend classes as often as desired, and one-on-one nutritional counseling is available.
BIMS Bariatric Surgery Program is pleased to provide patients, family, and friends with educational and support tools to help you maintain a healthy lifestyle. Support groups offer continued education through distinguished speakers and other post-surgery patients. The groups build a community for mentoring, additional support, and accountability.
Support group educational and fun events are coordinated by a licensed therapist. These groups can help you learn what to expect before, during, and after your surgery. We offer in-depth educational workshops on such topics as body image, weight maintenance skills, and relapse prevention. Specific groups for men, singles, couples, and families are offered.
Fun and interesting events planned on a semi-annual basis may include fashion shows, cooking demonstrations, and food shopping tips, a field trip, and holiday celebrations.
For convenience, evening support groups are held at several locations in the Dallas area. You may attend these support groups as often as you’d like at no charge.
- All patients are required to attend at least two before being scheduled for surgery
- Occur about every 2-4 weeks
- You’ll hear presentations made by clinical providers
- You’ll get answers to your questions and concerns
- You’ll learn about making positive changes to your eating
- You’ll learn what to expect after surgery
- Patients who already had the surgery answer your questions
- Offers a helping hand after your surgery
- Sessions dedicated to emotional issues
- Sessions dedicated to nutritional plans, concerns, and sharing of tips
Long-term follow-up care is the key to having the best outcome after bariatric surgery. Long-term success also depends on making life-long lifestyle changes, like diet and physical activity. Having regularly scheduled medical follow-ups will help you not only learn how to make these changes but sustain them as well.
Nutritional needs also change as weight loss occurs, and diet adjustments often need to be made without delay. Checking for and treating any vitamin and mineral deficiencies is also a must. Always check with your doctor before making changes to your diet, vitamins, and medications. Seeing your clinical team regularly allows them to work with you and provide excellent care.
What You Can Expect to Lose……..and Gain
Most of our patients lose between 60 and 80 percent of their excess body weight during the 18 to 24 months following surgery. But bariatric surgery is not a miracle cure, and you should not expect to have a “perfect” body or the one you had when you were 16. The weight loss you achieve can only be sustained with your commitment to dietary changes and regular exercise.
All facets of your life — body, mind, and spirit — will potentially undergo significant positive changes as a result of bariatric surgery. Your overall quality of life will improve. Many patients are thrilled to be able to do ordinary things again, like going to the store, playing with their children, getting in and out of a car easily, riding a bike, shopping for clothes off the rack, and more!
Yet some people find old feelings related to poor self-esteem, self-worth, or depression resurface. Our psychology staff will help you deal with those feelings so that you don’t fall back into old habits. We pledge to provide the support and direction you need to succeed in your weight-loss journey.
Common Bariatric Postoperative Concerns :
To help address some common bariatric postoperative concerns, here are some simple solutions or over-the-counter medication options that may help:
Fatigue:
You will need time to recover from your surgery. You may feel tired and it often takes several weeks to regain your usual energy level. Problems with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, low blood counts, and nutrition can combine to make you feel tired as well. The best thing to do is stay active. Walking can help your energy level. Plan to take 10-minute walks at least 6 times each day. Get 65-75 Gms of protein and 1500ml of fluids each day.
Constipation:
Patients often go several days after surgery before having a bowel movement. Do not be concerned unless your abdomen is feeling full and bloated or you have related discomfort. Increasing your activity and fluid intake will help. You may also purchase Colace or Cremaffin over the counter and take it as directed.
Diarrhea:
When bowel function returns it’s common to experience some diarrhea. Take your temperature and if you have a fever greater than 100’ F or you have severe abdominal cramping, call your surgeon’s office and leave a detailed message including your temperature and how often, the number of times, and how long you have been having diarrhea. If you do not have a fever, you may try over-the-counter medicines like Vibact, vizslas, or any Pre-probiotics. Take them only as directed by your doctor.
Gas/ Bloating/ Flatulence:
You may take Beano and Simethicone (Gas-X, etc.) as directed for these symptoms.
Nausea and Vomiting:
If you experience persistent nausea and/or vomiting, it’s best to switch your diet to clear liquids. If these symptoms last longer than 24 hours or you are unable to hold down clear liquids, contact your bariatric surgeon. Take prescribed anti-nausea medications, if you have them, as directed.
Mild Pain or Headache:
You may take Tylenol or Paracetamol as directed but ONLY use it if you are no longer using Narcotic pain medication.
Do not take Non-Steroidal Anti Inflammatory medications or NSAIDS particularly in Bypass surgery.’
Cold or Cough:
If you have a cold or cough in the first 6 weeks after your surgery, take your temperature and contact your bariatric surgeon. If you’re past6 weeks post-op and have a cold or cough symptoms, consult with a pharmacist to choose the proper medication for your symptoms. Be sure to explain that you cannot take Non-Steroidal Anti Inflammatory medications (NSAIDS) due to your surgery.
Menstrual Cramping:
If you have severe cramping, consult your gynecologist. Do not take Non-Steroidal Anti Inflammatory medications (NSAIDS). For cramping that is not severe, you may take Tylenol as directed and/or use a heating pad for relief.
Difficulty Swallowing or Food Intolerance:
If you have difficulty swallowing or eating, contact your surgeon.
Pregnancy after Bariatric Surgery:
It’s possible to have a safe and healthy pregnancy after bariatric surgery. In fact, some research suggests that pregnancy after weight-loss surgery might be safer for both mother and baby than pregnancy complicated by obesity.
Timing is important, however. It’s best to avoid pregnancy after weight-loss surgery until your weight is stable and it has been at least 2 years since your surgery. Rapid or persistent weight loss might deprive a growing baby of important nutrients, leading to low birth weight and problems.
Depending on the type of weight loss surgery and your specific nutritional needs, your health care provider might recommend certain nutritional supplements, such as folic acid, vitamin B-12, vitamin D, iron, and calcium, in addition to a daily prenatal vitamin before and during pregnancy.
You might also consult a registered dietitian for advice on nutrition and weight gain during pregnancy.
Hair Loss after Bariatric Surgery:
Bariatric surgery can result in rapid weight loss, which can place the body under physical stress. Most people notice changes in their hair after bariatric surgery, from a dull and lifeless appearance to actual hair loss. Because the body does not get the nutrients it needs through diet alone, it sends hair into a resting phase in order to save nutrients for vital organs. Any hair loss is usually temporary. Protein supplements, snacks, and shakes may help reduce hair loss after surgery, but almost everyone experiences some hair loss.
Managing Hair Loss
To manage any hair loss you may experience, maintain your protein intake at 65-70 grams daily. You can also use a hydrating shampoo and conditioner. Only shampoo your hair when needed. Avoid harsh chemical services such as color, perms, and relaxers. Cut back on thermal styling, and use
a thermal styling spray to protect the hair from heat damage. Also, get a good haircut. Removing several inches can make your hair appear thicker and healthier.
Medications like multivitamins, minerals, and Biotin can take daily at least the first year after Bariatric Surgery for Hair loss.
Loosening of skin and Plastic Surgery:
Weight loss leads to loosening of skin particularly after 1 year of post-bariatric surgery, more common in middle age and old age patients. Plastic surgery (body contouring surgery) is an option after bariatric surgery. Before this type of surgery can be done, weight loss needs to have stabilized and it needs to have been at least 1.5-2 years since your bariatric procedure. Types of surgery may include facelift, breast lift, tummy tuck- Abdominoplasty, lower body lifts, thigh lift, and Brachioplasty (arm lift). Talk to your bariatric surgeon for plastic surgeon recommendations.
Obesity Surgery – FAQ
What is the best surgery to lose weight?
Bariatric surgery remains the proven best when compared to the other types of surgery as it aids definite results and quicker recovery. The principle of this weight loss surgery is to confine the intake of food and drink and to limit the absorption of the food in the intestine and thus aid weight loss.
How do operations reduce fat?
Obesity Surgery – Weight loss operations proceeds by reducing the size of the stomach by removing a part of it or by resecting and re-routing the small intestine to a smaller pouch. They don’t essentially reduce fat but restrict the net intake which would aid the same.
Can belly fat be removed by surgery?
Obesity Surgery – Bariatric procedures are done for aiding weight loss by removing or redirecting a part of the stomach pouch. It is different from tummy tuck procedures which involve abdominal wall surgery or liposuction operations.
Is Bariatric Surgery Safe?
Through the advancements of laparoscopic methods, bariatric surgery is now being carried out through minimally invasive methods. It thus remains the safest option among the other weight loss options
Can you eat normally after gastric bypass?
Post-op care must be given prominent importance after the procedure. The net food intake reduces drastically and hence the patients must be conscious for a brief period before resuming their normal food behavior.
How Dangerous Is Weight Loss Surgery?
Just like any other surgery, weight loss procedures also have their own associated health risks. The short-term risk factors include excessive bleeding, inflammations, and infections. Through advanced laparoscopic techniques, these complications can be eliminated.
How overweight do you need to be for surgery?
Patients with BMI beyond 37 are prone to a lot of ailments associated with obesity like diabetes, heart diseases, hypertension, etc., These patients can opt for bariatric surgery and can achieve weight loss within a short period of time.
What is the best way to remove stomach fat?
The bariatric procedure has been proven effective to aid permanent weight loss without much complications like other procedures. It can also potentially aid shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery
Why do gastric bypass patients lose weight so fast?
The size of the stomach is reduced in this procedure through surgical resection. Thus the net food intake and nutrient absorption are reduced permanently aiding faster weight loss compared to other procedures.
Can you gain weight back after gastric bypass?
A part of the stomach pouch has been permanently removed from the digestive tract and hence it restricts the net food intake. Hence, gaining weight back does not happen after the procedure
Top Bariatric And Diabetes Surgeon Bhavnagar
Dr. Vijayrajsinh Gohil
MS, FNB, FMAS, FIAGES, FACS, FALS, FMBS, Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery (Taiwan)G I and Laparoscopic Surgeon
Bariatric and Metabolic Surgeon
