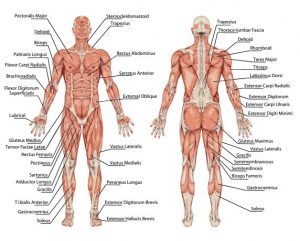
Department of Orthopaedics/ Trauma
Orthopaedics:
- A department that specializes in easing the joint and bone pain.
- Our orthopedic surgeons use surgical techniques to reduce recovery time and offer timely medical guidance.
- Among the list of specialties, common procedures involve knee surgery, shoulder surgery, hip surgery, and hand surgery.
Orthopaedic is the field of medical that focuses on disease and conditions that affect your musculoskeletal System. This includes you’re:
- Bones
- Muscles
- Ligaments and tendons
- Joints
- Nerves
People often visit an orthopaedic doctor when they are injured or when they have a chronic conditions, such as arthritis or lower back pain.
WHAT ORTHOPEDIC DOCTORS DO?
Orthopaedic doctors, often referred to as orthopaedic surgeons, focus on helping you with musculoskeletal issues. Their duties include:
- Diagnosing and treating conditions that affect your musculoskeletal system
- Assisting with rehabilitation, which helps you regain movement, strength, range of motion and flexibility following and injury or surgery.
- Forming strategies to prevent injury or to keep chronic conditions, such as arthritis from worsening.
While orthopaedic doctors know about all part of the musculoskeletal system, some choose to specialize further. Some subspecialty areas of orthopaedics include:
- Spine
- Hip and Knee
- Hand
- Shoulder and elbow
- Foot and ankle
- Sports medicine
- Trauma Surgery
WHAT TYPES OF CONDITIONS DO ORTHOPEDIC DOCTORS TREAT?
Orthopaedic doctors treat a wide variety of conditions, including but not limited to the following:
- Bone Fracture
- Muscle strains
- Joint OR back Pain
- Arthritis
- Injuries to tendons or ligaments, such as sprains, tendonitis, and ACL tears
- Limb Abnormalities, such as clubfoot and bowlegs
- Bone Cancer / Bone Tumour
- SPORTS INJURIES
WHAT TYPES OF PROCEDURES ORTHOPAEDIC DOCTORS DO?
Orthopaedic doctors recommend a variety of treatments and procedures for the conditions they handle.
- NONSURGICAL TREATMENTS:
- These types of treatments are also called conservative treatments. Orthopaedic doctors will often focus on nonsurgical treatments first before recommending surgery.Some types of nonsurgical treatments include
- EXERCISES:
Your orthopaedic doctor may recommend specific exercises or stretches to help maintain or improve your strength, flexibility, and range of motion in particular area.
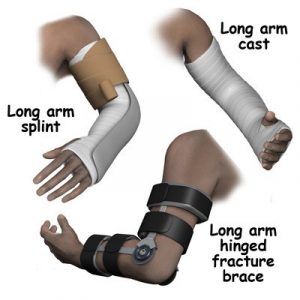
- IMMOBILIZATION:
Sometimes preventing additional strain to an area can help it to heal. Examples of immobilization techniques include braces, splints, and casts.
- MEDICATIONS:
Your Orthopaedic doctor may recommend certain medications to help relieve symptoms like pain and swelling. Some examples include over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen and aspirin. They may also prescribe certain prescription drugs like corticosteroids and anti-inflammatory medicine.
- LIFESTYLE CHANGES:
Your orthopaedic doctor may also help you with making lifestyle changes. These can involve modifying your physical activity, diet, and the way you exercise to prevent aggravation of n injury or condition.
- SURGICAL TREATMENTS:
- Sometimes a condition or Injury doesn’t improve with conservative measures. In these cases, your doctor may recommend surgery. Some Example of operations performed by an orthopaedic surgeon includes:
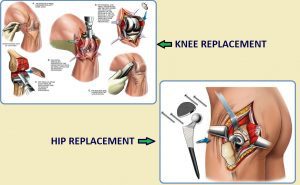
- JOINT REPLACEMENT:
Joint replacement surgery involves replacing the part of a joint that have become damaged or diseased, usually secondary to arthritis. Examples include knee replacement and hip replacement surgery.
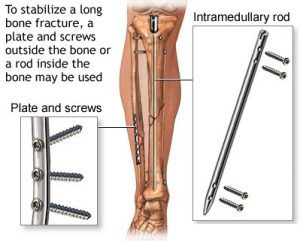
- INTERNAL FIXATION:
Internal fixation involve the placement of hardware such as pins, screws, plates, and rods to help hold broken bones in place while they are healing.
- FUSION:
This involves using bone graft material plus some form of internal fixation to connect two bones together. As the bone tissue heals, if fuses into one bone. This technique is often used in neck and spine surgery.
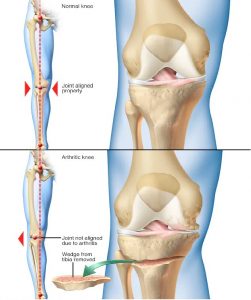
- OSTEOTOMY:
Osteotomy is a type of surgery that involves cutting a part of a bone and then repositioning it. This type of surgery may sometimes be used to treat arthritis.
- SOFT TISSUE REPAIR:
This king of surgery is used to repair severely damaged muscles, ligaments, or tendons.
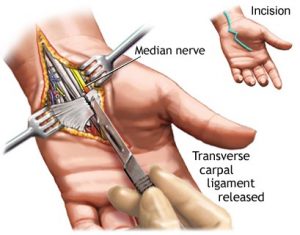
- RELEASE SURGERY:
This is a type of surgery that’s performed for carpal tunnel syndrome. It helps to relieve symptoms by reducing pressure on the median nerve.
WHEN TO SEE AN ORTHOPAEDIC DOCTOR?
You may need to see an orthopaedic doctor if you have:
- Pain or swelling in a bone, joint or muscle that’s persistent, recurring, or doesn’t respond to at-home care.
- A significant decrease in the mobility or range of motion of a join, such as your knee, elbow or Shoulder.
- Trouble performing your daily activities.
- Nerve-related symptoms, such as numbness and tingling or Pins and needles sensation in your arms or Legs.
- An injury to a bone or joint that needs the attention of a specialist.
ORTHOPAEDIC DIAGNOSTIC TESTS:
Orthopaedic Doctors use a variety of diagnostic tests to help identify the specific nature of your musculoskeletal injury or condition. Orthopaedists also use results of these tests to plan an appropriate course of treatment. Here are some of the most frequently used diagnostic test for musculoskeletal injuries and conditions.
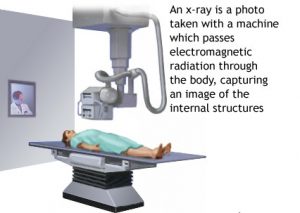
- RADIOGRAPHS (X-Rays):
X-Rays (Radiographs) are the most common and widely available diagnostic imaging technique. Even If you just complain about a sprain in your wrist or ankle, your doctor will probably order rediographs to make sure no bone is broken. X-Rays are always used for fractures and joint dislocations, and may also be recommended if your doctor suspects damage to a bone or joint from other conditions such as arthritis. The part of your body being pictured is positioned between the X-ray machine and photographic film. As you hold still, the machine briefly sends electromagnetic waves (Radiation) through your body. This expose the film, creating a picture of your internal structure. The level of radiation exposure from X-Rays is minimal, but your doctor will take special precautions if you are pregnant. Bones, tumours and other dense matter apper white or light because they absorb the radiation. Soft tissue and breaks in bone let radiation pass through, making these parts look darker.
- BLOOD TESTS:
As part of your examination, your orthopaedist may order a variety of blood tests. Some conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, may be identified by the presence of a specific substance in your blood. Usually a blood test is a simple matter that involves withdrawing a small amount of blood from your arm.
- MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI):
An MRI uses magnetic fields and a sophisticated computer to take high-resolution picture of your bones and soft tissues, resulting in a cross-sectional image of your body. It can be used to help diagnose torn muscles, ligaments and cartilage, herniated disks, hip or pelvic problems and other conditions. As with a CT scan, you lie on a table that slides into the tube-shaped MRI scanner. The MRI creates a magnetic field around you, then pulses radio waves to the area of your body to be pictured. The radio waves cause your tissues to resonate. A computer records the rate at which your body’s various part (tendons, ligaments, nerves) give off these vibrations, and translated the data into a detailed, two dimensional picture.
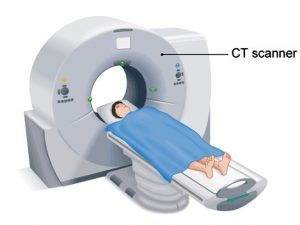
- CT SCAN:
A CT Scan (Computed Tomography) combines X-rays with computer technology to produce a more detailed, cross-sectional image of your body. It may be ordered if your doctor suspects a tumour or a fracture that doesn’t appear on X-rays or if you have had severe trauma to the chest, abdomen, pelvis or spinal cord. The process is painless. You may need to drink or be injected with barium sulphate or a dye so that certain parts of your body can be seen more clearly.
- DOPPLER ULTRASOUND :
An orthopaedist who suspects that you have a blockage in the blood vessels of your legs or arms may prescribe an ultrasound test. An ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves that echo off the body. This creates a picture of the blood vessels. The Doppler audio system transmits the “swishing” sound of the blood flow. This is a non-invasive test that has no side effects.
A clear jelly is applied to the skin over the blood vessels being tested. The technician uses a sensor that looks like a microphone. The sensor is placed against the skin and moved up and down across the area being tested. The technician will apply pressure every few inches to see if the blood vessels change their shape. The test take about 30 minutes and most people experience no pain or discomfort.
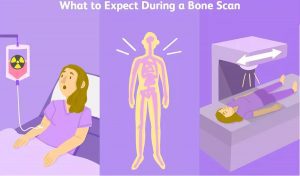
- BONE SCAN
There are two very different kinds of tests may be called bone scans. One type tests the density of the bone and is used to diagnose osteoporosis. This type of bone scan uses narrow X-ray beams or ultrasound to see how solid the bone is. No preparation is required for this test, which takes only a few minutes and has no side effects.
The second type of bone scan is used to identify areas where there is unusually active bone formation. It is frequently used to pinpoint stress fracture site or the presence of arthritis, infection or cancer. Abour three hours before the scan, you will be given a dose of mildly radioactive substance call “Technetium” through an intravenous line (IV). This substance occurs naturally in your body and is used in the bone formation process. The Bone scan itself is performed about three hours later, which gives the bone time to absorb the technetium.
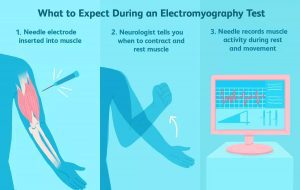
- ELECTROMYOGRAPHY:
EMG records and analyzes the electrical activity in your muscles. It is used to learn more about the functioning of nerves in the arms and legs. For Example, a fracture of the upper arm bone (Humerus) may tear or pinch the radial nerve. An EMG can be used to identify the damage if nerve function doesn’t return within 4 months of the injury.
- FLEXIBILITY TESTS:
Flexibility tests are used to measure the range of motion in a joint and are often part of the physical examination. They may be used to help determine whether you have a muscle imbalance or arthritis in a joint. They may also be used to help determine the progression of a condition such as shoulder impingement or a sprain. There are several different kinds of flexibility tests, geared to specific joints and muscles. Your doctor may ask you to reach or bend or to move the affected extremity in certain way.
- MUSCLE TESTS:As our muscles are soft tissues, they do not appear on X-rays. So muscle testing is an important part of the physical examination. Weakness in a muscle may indicate injury to the tendons that connect the muscle to bone, injury to the nerves that enervate the muscle, or a generalized weakness of the muscle itself from disuse.
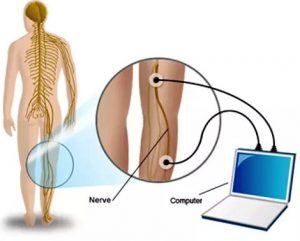
- NERVE CONDUCTION STUDY (NCS):
Nerve conduction studies are often done along with an electromyogram to determine if a nerve is functioning normally. It may be recommended if you have symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome or ulnar nerve entrapment. The doctor conducting the test will tape wires (Electrodes) to the skin in various places along the nerve pathway. Then the doctor stimulates the nerve with an electric current. As the current travels down the nerve pathway, the electrodes placed along the way capture the signal and measure its speed. In healthy nerves, electrical signals can travel at speeds of up to 120 miles per hour. If the nerve is damaged, however, the signal will be slower and weaker. By stimulating the nerve at various places, the doctor can determine the specific site of the injury. Nerve conduction studies also may be used during treatment to test the progress being made. Although you may initially be startled by the suddenness of the stimulation, it is not usually painful and most people are comfortable during the testing procedure. The shock is similar to one received when you touch a doorknob after walking across carpeting.
- PHYSICAL EXAMINATION:Your physician can tell a lot about your health simply by looking at you. Obvious signs and symptoms include weak (Atrophied) or asymmetrical muscles, improper alignment, swelling, changes in skin color (such as bruises or redness that might indicate inflammation) and growths such as cysts, calluses or corns. But the physical examination is much more than just cursory look. It can also involve gait analysis (how to walk), palpation, muscle testing, flexibility (range of motion) testing, reflex response, and laboratory tests such as a complete blood count and urine analysis.
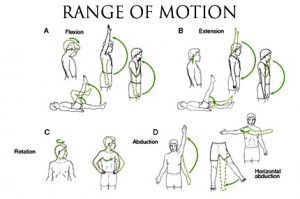
- RANGE OF MOTION TESTING:
Range of motion tests may also be called flexibility tests. They are used to measure how well you can move a joint. Some joints like the thumb and shoulder have a wide range of motion, almost a complete circle. Other joints llike the knee are like hinges and have a more limited range of motion. Range of motion tests may be active or passive. In active tests, you do all the movement. In passive tests, the doctor will hold the extremity and move it.
PREVENTIVE ORTHOPADIC CARE:
Making a Few simple changes to your diet and lifestyle can help you avoid serious orthopaedic problems:
- MAINTAIN A HEALTHY WEIGHT: For every 10lbs. of weight gained, there is a 36% increased risk of developing osteoarthritis. Obesity also puts more weight on your joints, which can weaken muscles and make injuries more likely.
- KEEP IT MOVING: Exercises of everyone – even those with some orthopaedic sensitivity- include stretching, walking, swimming on a level ground. Try to avoid exercises that put too much stress on your joints, like deep knee bends. But keep working to increase muscle mass no matter your age.
- DEVELOP A STRONG CORE:Strong core muscles help you balance your body weight. Yoga and pilates are two good kinds of exercise to strengthen your core and promote orthopaedic health.
- STRETCH BEFORE EXERCISE:Stretching is important to maintain flexibility, improve performance and decrease stress injuries like Sprains and strains. If you are going to lift weights or do high impact aerobics, work on warm up and stretching exercises before and after exercise. These types of exercises promote increased flexibility and help prevent muscle and joint injuries.
- WEAR COMFORTABLE SHOES:Supportive shoes promote proper alignment. Women who wear high heels on regular basis increase their rist of developing back pain and knee pain.
- GET REGULAR CHECKUPS:Yearly visits to your primary care doctor are one great way to stay on top of your orthopaedic health. This is especially important for older adults, who can be more likely to develop arthritis and suffer injuries. A primary care doctor can discuss additional preventive measures to protect your orthopaedic and overall health.
DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY @ BIMS
Bhavnagar Institute of Medical Science (BIMS) is the centre of excellence in orthopaedics and joint replacement surgery in this part of Gujarat. With its latest technologies and state-of-art equipments, department of orthopaedic surgery is delivering excellent outputs for their patients at BIMS hospital. Our numbers only suggest that our patients trust the services provided by our team of consultant and supporting staff at BIMS, Bhavnagar.
Apart from being the unbeatable joint replacement surgery centre in Bhavnagar, BIMS hospital provides a wide range of orthopaedic surgery to serve patients that include surgeries like:
- COMPLEX FRACTURE SURGERIES:
- Fracture fixation with minimal invasive technique
- Polytrauma surgeries
- Pelvi-acetabular Surgeries
- Spine fracture fixation
- Complex intra articular fracture management
- JOINT REPLACEMENT SURGERIES (ARTHROPLASTY)
- Total Knee replacement (TKR)
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Unicondylar Knee replacement (UKR)
- Total Shoulder / Elbow replacement (TSR / TER)
- Hemi Arthroplasty of Hip and Shoulder
- Minimal invasive Arthroplasty
- Navigation based joint replacement surgeries
- JOINT PRESERVATION PROCEDURE:
- Proximal tibial osteotomy (PTO)
- Knee Arthroscopy
- Intra articular vissco supplement injection
- SPORTS MEDICINE AND ARTHROSCOPIC SURGERIES:
- Meniscus injury
- ACL Injury (Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury)
- Shoulder Instability (recurrent shoulder dislocation)
- Rotator cuff surgery of shoulder
- Multi ligament knee surgeries
- PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERIES:
- Congenital anomalies of upper and lower limb
- CTEV and Flatfoot surgeries
- Congenital and developmental deformities
- Fractures of children
- Metabolic disorder like rickets, scurvy, etc management
- ORTHO-ONCO UNIT:
- Paediatric & adult bone tumour surgeries
- Malignant & benign tumour management
- Limb salvage surgery
- Mega prosthesis / Tumour prosthesis
- DEFORMITY CORRECTION SURGERIES:
- Corrective osteotomies by Ilizarov method
- Computer assisted limb lengthening surgery
- Angular deformity correction surgery
- Post traumatic deformity correction surgery
BIMS hospital has team of experienced orthopaedic surgeons who has specialized in different specialities with fellowships – training – research programmes. Apart from in-house 3 experienced orthopaedic surgeons, we have list of renowned Super Specialist orthopaedic surgeons visiting BIMS regularly and performing the most advanced surgeries here. To support department’s work, we have team of dedicated medical officers and Physiotherapist who constantly support patients in their pre and post operative period.
For Orthopaedic patients, BIMS hospital has unique facilities which support orthopaedic surgeons efforts to bring 100 % results. Some of which are as follows:
- DIGITAL X-RAY WITH FULL LENGTH AND STANDING X-RAY FACILITIES
- CT-SCAN
- MRI
- DEXA SCAN
- SIEMENS C-ARM (IITV)
- ARTHROSCOPY SYSTEM (SHOULDER AND KNEE) – SMITH & NEPHEW
- RF SYSTEM
- REVISION REPLACEMENT SURGERY INSTRUMENTS
- SYNTHES AND STRYKER BATTERY OPERATED DRILL SYSTEMS
- EXHAUST VENTILATION HELMET SYSTEM
- SPINE AND PELVI-ACETABULAR SURGERY INSTRUMENTS
- OT COMPLEX WITH FOUR MODULAR OTS
- CSSD DEPARTMENT WITH ETO MACHINE
To support Post operative care, BIMS has advance physiotherapy rehabilitation center with team of dedicated physiotherapist and latest equipments up to LASER Therapy. At this department, preventive as well as therapeutic care is given especially taking care of joint replacement surgery Patients, Post ligament surgery patients, post fractures rehabilitation etc.
Trauma:
- This department provides around-the-clock treatment for patients with critical conditions.
- The department has dedicated physicians and staff to provide the best possible care to all types of traumatic and non-traumatic injuries.

Top Orthopedic Surgeons Bhavnagar
Dr. Sanjiv Ravisaheb
M.S (Orthopaedics), F.I.A. (Seoul, S. Korea), F.I.A.A. (Endoklinik, Hamburg, Germany)Orthopaedics
Dr. Harshvardhan Jadeja
M.S. Orthopaedics, M.Ch. Orthopaedics, Fellow in Arthroplasty (UK. Italy), Certificate Course in Rheumatology, Fellow in Arthroscopy (SportsMed, Mumbai)Orthopaedics
Dr. Suresh Parmar
Fellowship Spine (New Delhi) Orthopaedics Surgeon Trauma & SpineOrthopaedics